Fixed-rate mortgages are a popular choice for homebuyers seeking stability and predictability in their monthly payments. Unlike adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), which can fluctuate over time, fixed-rate mortgages maintain the same interest rate for the entire loan term. This guide will explain what fixed-rate mortgages are, their benefits, how they work, and tips for choosing the right fixed-rate mortgage for your needs.
What is a Fixed-Rate Mortgage?
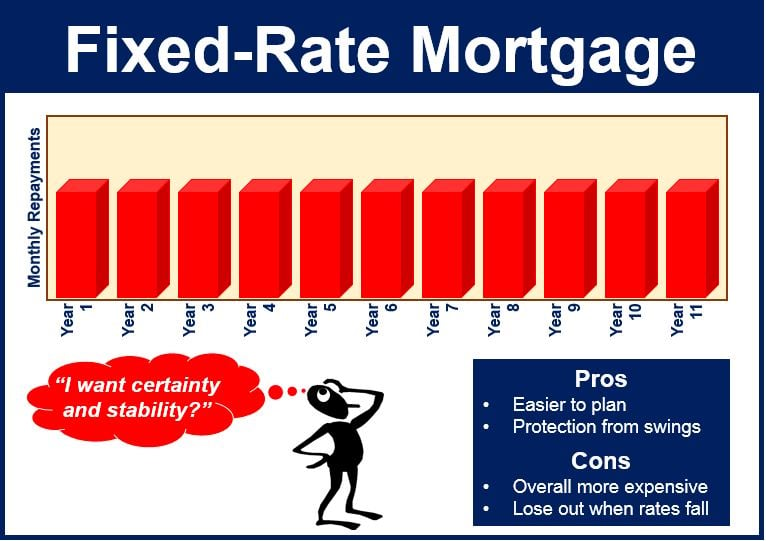
A fixed-rate mortgage is a home loan with an interest rate that remains constant for the entire term of the loan. This means that the principal and interest portion of your monthly mortgage payment will not change, providing predictability and stability for your budgeting.
Benefits of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
- Predictable Payments: With a fixed-rate mortgage, your monthly principal and interest payments remain the same throughout the loan term, making it easier to plan and budget.
- Protection Against Rising Interest Rates: If interest rates increase, your rate remains unchanged, protecting you from higher payments.
- Long-Term Stability: Fixed-rate mortgages offer long-term financial stability, making them ideal for homeowners who plan to stay in their homes for an extended period.
- Simplicity: Fixed-rate mortgages are straightforward and easy to understand, with no surprises or adjustments to worry about.
How Fixed-Rate Mortgages Work
Fixed-rate mortgages are characterized by their unchanging interest rate and consistent monthly payments. Here’s how they work:
- Loan Term: Fixed-rate mortgages are typically available in various terms, with 15-year and 30-year terms being the most common. Shorter terms generally have higher monthly payments but lower total interest costs, while longer terms have lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate is set at the time you take out the loan and does not change for the duration of the loan term. The rate you receive depends on factors such as your credit score, loan amount, down payment, and current market conditions.
- Amortization: Fixed-rate mortgages are fully amortizing, meaning that each monthly payment includes both principal and interest, and the loan will be paid off in full by the end of the term.
Example of Fixed-Rate Mortgage Payments
Consider a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage of $300,000 with an interest rate of 4.0%:
- Monthly Payment: $1,432.25 (excluding taxes and insurance)
- Total Payments Over 30 Years: $515,610
- Total Interest Paid: $215,610
The monthly payment remains the same for the entire 30-year term, providing stability and predictability.
Choosing the Right Fixed-Rate Mortgage
When selecting a fixed-rate mortgage, consider the following factors:
- Loan Term: Decide whether a 15-year, 20-year, or 30-year term suits your financial situation and long-term goals. Shorter terms save on interest but have higher monthly payments, while longer terms offer lower payments but cost more in interest over time.
- Interest Rate: Shop around for the best interest rates. Compare offers from multiple lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Your credit score, down payment, and loan amount will affect the rate you receive.
- Down Payment: A larger down payment can help you secure a lower interest rate and reduce your monthly payments. Aim for at least 20% to avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI).
- Fees and Closing Costs: Consider the fees and closing costs associated with the loan. These can include origination fees, appraisal fees, and title insurance. Some lenders may offer lower rates but higher fees, so evaluate the overall cost.
- Lender Reputation: Choose a reputable lender with good customer service. Read reviews and seek recommendations to ensure a smooth and reliable mortgage process.
Fixed-Rate Mortgage vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgage
While fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) provide initial lower rates that can change over time. Here’s a comparison:
- Interest Rate: Fixed-rate mortgages have stable rates; ARMs have rates that adjust after an initial fixed period (e.g., 5/1 ARM, 7/1 ARM).
- Monthly Payments: Fixed-rate mortgage payments remain the same; ARM payments can increase or decrease based on market conditions.
- Suitability: Fixed-rate mortgages are ideal for long-term homeownership; ARMs may be suitable for short-term ownership or if you expect interest rates to remain stable or decrease.
Conclusion
Fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, predictability, and long-term financial security, making them a popular choice for many homebuyers. By understanding how fixed-rate mortgages work and considering factors such as loan term, interest rate, and fees, you can choose the right mortgage to fit your needs. Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer or refinancing an existing mortgage, a fixed-rate mortgage can provide the peace of mind that comes with consistent monthly payments and protection against rising interest rates.